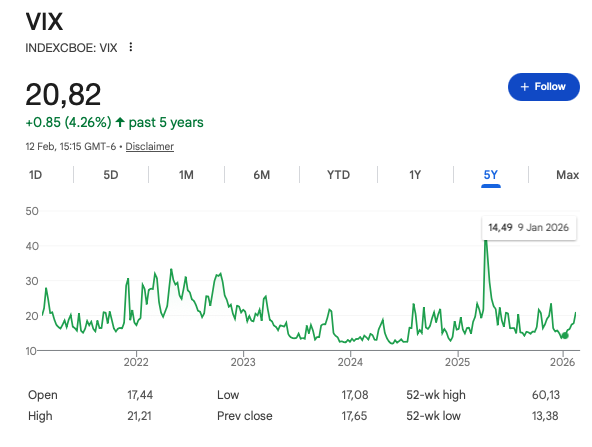
Alphabet (GOOG, GOOGL) has captured significant legal interest, driven by its dominance in search, cloud computing, and its ongoing ventures into AI. While the company remains fundamentally strong, recent market dynamics have prompted a more strategic approach to trading its stock. Instead of predicting a potential outcome of the recently disclosed legal battles, we recommend a long put option strategy to capitalize on potential downside movements in GOOG’s stock price or to hedge a long equity position. Specifically, we focus on the Sep 19 '25 170 put option, trading at a premium of $13.85. This approach offers a defined risk profile and the potential for attractive returns or floor/protection against losses if the stock declines significantly. Alphabet Inc., continues to lead the global technology space, with revenue streams spanning advertising, cloud computing, and emerging technologies like autonomous driving (via Waymo) and generative AI. The company has maintained robust financial health and innovation capacity, but macroeconomic challenges and regulatory scrutiny pose potential headwinds. Recent market volatility, driven by concerns about rising interest rates and global economic uncertainty, has impacted GOOG's valuation. Despite these fluctuations, the company’s fundamentals remain strong, making the current market scenario a prime opportunity for options-based strategies. In this short article we’ll not discuss the valuation of the company, yet we’ll focus on a specific investment strategy - hedge if you will. Several factors could influence GOOG's stock price in the coming months: Investor may fear the possible decline of GOOG/GOOGL stock price in the near future. A critical motivation lies in the heightened regulatory and legal pressures Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) is facing as stated above. The U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) has escalated its antitrust case against Google, seeking "structural remedies" to address the company’s dominant market position. Among the measures reportedly under consideration are demands for Google to divest its Chrome browser and implement new restrictions related to AI and its Android operating system. If these proposals are accepted by the federal judge overseeing the case, they could lead to a significant reshaping of Google’s core business model. The mandated divestiture of Chrome, a key element of Google's internet ecosystem, and potential constraints on AI operations, could reduce the company’s revenue streams and competitive advantages. The prospect of such sweeping changes introduces considerable downside risk to the stock price. The legal timeline is as follows: first judgment expected for August 2025; Alphabet stated already that they will appeal the judgment. Hence the litigation is expected to be protected for years (3, 5 or 7 years as per legal history). Hence the first action date to consider is August 2025. As you may know, an option is a financial derivative that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price (called the strike price) before or on a specified expiration date. There are two types of options, namely: call and put. A put option specifically grants the holder the right to sell the asset at the strike price. Investors use put options to hedge against downside risk or to speculate on a decline in the asset's price. If the price falls below the strike price, the put increases in value, allowing the holder to sell the asset at a higher-than-market price. Conversely, if the price remains above the strike price, the put expires worthless, and the loss is limited to the premium paid for the option. Right now options after the first expected legal action date of August 2025, are available for September 19, 2025. In particular, the Sep 19 '25 170 put option, priced at $13.85 at last market close on Friday, November 29, 2024, provides an excellent way to hedge against or profit from potential downside risks. Here’s why this strategy is intriguing:TL;DR in 4 Points, plus one:
Summary
Company Overview
Key Market Dynamics
Main Motivation for an Hedging Strategy
Why Consider a Long Put?
By choosing the Sep 19 '25 170 put, we position ourselves to benefit from potential price declines while maintaining a controlled risk profile. The strike price of $170 is at-the-money (or ATM). Considering the long time to expiration though, we indirectly assume that the company will not only decline in price in case of an unfavorable legal sentence, but also stall during the previous 8-9 months. Nonetheless, it offers a compelling risk-reward balance. Break-even Point: It will realistically be lower if accounted for a generic 0.04% transaction fee (hence BE of $155.53). Considerations: You can be interested in such a strategy either if you want to purely play the future event and speculate the stock price will tumble as a consequence of the legal battle. The other possibility is that you hold a direct interest in the company (i.e. you are a direct equity owner of GOOG/GOOGL shares) and you want to protect from downside risk - hedging. Both circumstances are also viable for strategies different from this one, and you should not take this as financial advice nor a recommendation to invest in the option or the company. This material is for entertainment purpose only. Investors holding GOOG/GOOGL shares, particularly those with a significant stake such as 100 shares, are directly exposed to potential downside risk stemming from the ongoing antitrust litigation. A long put option, such as the Sep 19 '25 170 put with a premium of $13.85, serves as a protective hedge to mitigate this risk. Here’s how the strategy could play out under two plausible scenarios: Scenario 1: Google Loses the Legal Battle Should the DoJ's case succeed and the proposed structural remedies be enforced, GOOGL's stock price could experience a sharp decline. The holder of the put option benefits from the downside protection it provides. For instance, if GOOGL’s stock price falls below $170, the put option becomes increasingly valuable, offsetting a portion of the losses incurred on the equity position. While losses from holding the shares are inevitable, they are effectively capped at a fixed percentage (to be calculated based on the specific position and option details), thanks to the hedge provided by the put. In particular if you hold 100 shares of the company, calculation results in an effective floor to the losses, as shown in the images below. In case the investor hold less shares, the profit line of the hedged position diverge positively with the potential of making a substantial profit. Image below is computed with 50 shares. If the share owned are more than the 100 covered in the option contract, then the loss is just tamed and not fully capped. Image below is computed with 150 shares. Scenario 2: Google Wins or the Market is Unmoved If Google successfully defends itself (it stated already that it plans to appeal to the first judgment) or the litigation does not result in a material impact on the stock price, the put option will expire worthless. In this case, the investor’s upside from their 100 shares of GOOGL remains intact, albeit slightly reduced by the $13.85 premium paid for the put option (i.e. $1’385). Regarding the incoming DOJ prosecution on the alleged GOOG monopoly, we’d like to share our perspective: Given the regulatory uncertainty and the potential for significant market volatility, implementing a protective long put strategy allows GOOGL shareholders to balance risk and reward effectively. The hedge provides peace of mind by capping potential losses in the event of a drastic stock price decline while allowing for participation in the upside, albeit with a modest reduction in net gains due to the premium paid. This proactive approach ensures that investor is prepared for both outcomes—whether the litigation culminates in a landmark antitrust ruling or ultimately fizzles out. The strategy shows a useful case of leveraging options as a tool for managing risk, particularly when navigating uncertain market conditions with binary outcomes. The investor should use this as a pure option play on GOOGL downside or as a temporary hedge against transient stock price volatile. Indeed the investor should question why she/he is holding the stock. Does he/she believe the Company will survive the legal battle and thrive in the subsequent years? Disclaimer: I am not a financial advisor or registered investment advisor. The information contained in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results. You should always conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. Disclosure: I/we are long GOOG, GOOGL, MSFT.
Tailoring the Strategy
Managing Equity Exposure with a Protective Long Put






Balancing Risk and Reward